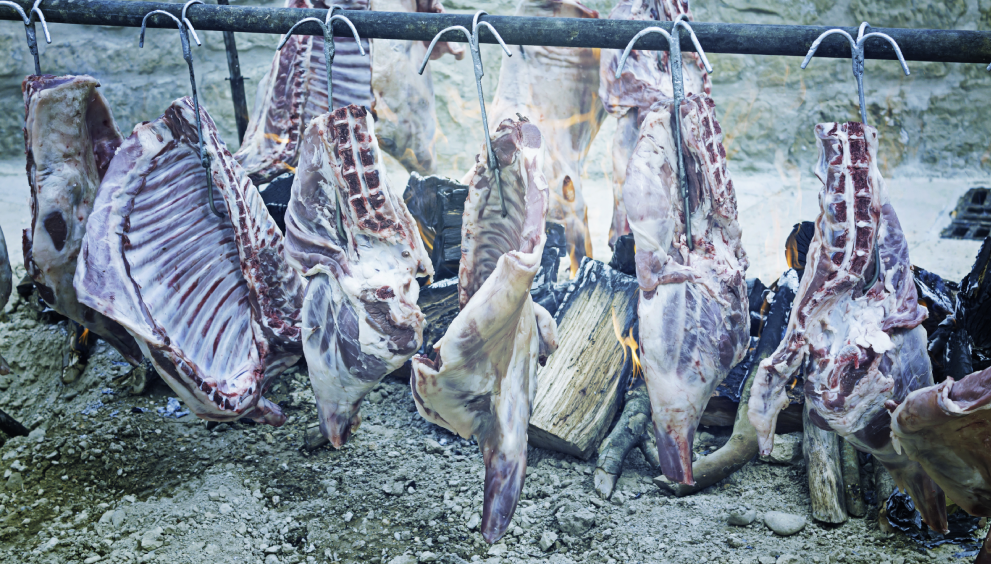
Why Humane Slaughter Matters in Halal Practices
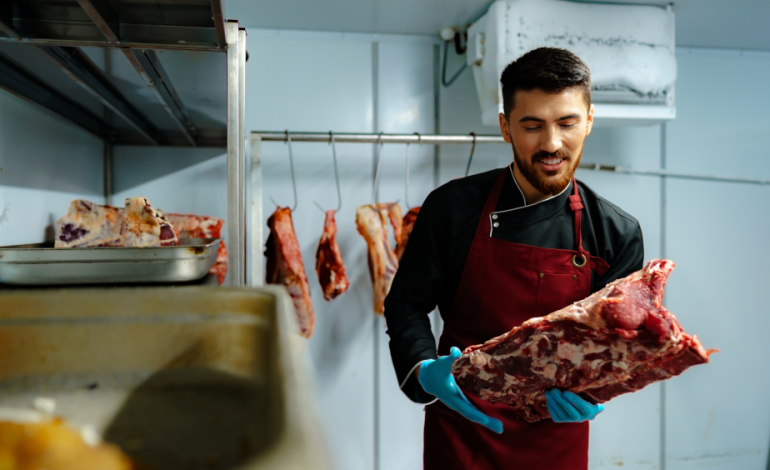
Humane slaughter is at the heart of Zabiha certification. Beyond religious compliance, it ensures animal welfare, meat quality, and consumer confidence. Understanding why humane practices are critical helps slaughterhouses maintain ethical standards and uphold Halal integrity—especially when sourcing from trusted halal food providers like Hilal Caters, a company that sells halal food and catering services.
The Religious Foundation
Islamic law emphasizes compassion and minimizing suffering. Halal slaughter requires that animals are treated with respect throughout their lives and during the act of slaughter. Humane treatment is not optional—it is a requirement. Animals must be healthy, stress-free, and handled gently.
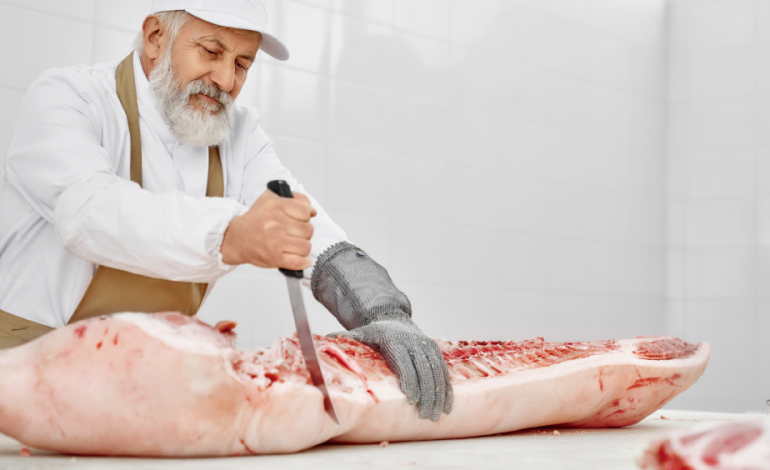
Swift, careful slaughter that fully drains blood while invoking Allah’s name fulfills religious obligations and reflects ethical responsibility.
Impact on Animal Welfare
Humane slaughter significantly reduces pain and distress. Proper handling, calm restraint, and quick slaughter prevent fear, injury, and suffering. Stress-free animals are not only treated ethically but also produce higher-quality meat.
Unethical treatment—rough handling, prolonged restraint, or slow slaughter—violates Halal principles and can compromise the facility’s certification.
Benefits for Meat Quality
Stress before slaughter triggers the release of hormones like cortisol, which can affect meat texture, color, and shelf life. Humane practices reduce stress, resulting in:
- Tender, well-textured meat
- Improved flavor and freshness
- Longer shelf life and safer consumption
Slaughterhouses that prioritize humane practices therefore deliver both ethical and commercial benefits.
Consumer Trust and Market Value
Consumers increasingly demand transparency in meat sourcing. Zabiha-certified meat that emphasizes humane slaughter builds trust among buyers, families, and retailers. Facilities that demonstrate ethical standards differentiate themselves in competitive markets and often gain loyalty and repeat business.
Humane practices also align with global animal welfare expectations, allowing facilities to expand into international Halal markets.
Training and Oversight
Implementing humane slaughter requires trained staff. Personnel must understand proper handling, restraint, and slaughtering techniques. Supervisors should monitor processes to ensure standards are consistently applied.
Regular training updates, audits, and record-keeping are essential for maintaining accountability and meeting Halal certification requirements.
Compliance and Ethical Standards
Humane slaughter aligns with both religious and regulatory standards. Halal authorities often evaluate animal welfare as part of their certification inspections. Facilities that neglect humane practices risk failing audits, losing certification, and damaging their reputation.
Embedding ethical slaughter practices into daily operations ensures compliance, improves meat quality, and enhances consumer confidence—benefiting both the facility and the broader Halal community.
Conclusion
Humane slaughter is a cornerstone of Halal practices, reflecting religious, ethical, and commercial priorities. It ensures animals are treated with respect, maintains meat quality, and builds consumer trust.
For Zabiha-certified slaughterhouses, prioritizing humane slaughter is not just about compliance—it is about integrity, professionalism, and commitment to ethical standards. By doing so, facilities uphold the true spirit of Halal, benefiting animals, consumers, and their business alike.